How Do You Know When Your Period Is Over
Understanding how flow works can assistance yous understand how your own cycle works.
Your menstrual cycle is part of your body's way of preparing for a possible pregnancy each month. Understanding how the process works is of import, since you can utilise this data to aid to either get meaning or avoid getting pregnant, to better manage any menstrual symptoms yous are experiencing, and empathize when at that place might be a problem.
What is menstruation?
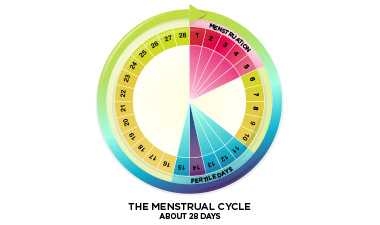 Menstruation is the technical term for getting your flow. Most once a month, females who accept gone through puberty will experience menstrual bleeding. This happens considering the lining of the uterus has prepared itself for a possible pregnancy by becoming thicker and richer in claret vessels. If pregnancy does non occur, this thickened lining is shed, accompanied by bleeding. Bleeding usually lasts for 3-viii days. For most women, menstruum happens in a adequately regular, predictable blueprint. The length of fourth dimension from the first mean solar day of one menstruation to the beginning day of the side by side menstruum normally ranges from 21-35 days.
Menstruation is the technical term for getting your flow. Most once a month, females who accept gone through puberty will experience menstrual bleeding. This happens considering the lining of the uterus has prepared itself for a possible pregnancy by becoming thicker and richer in claret vessels. If pregnancy does non occur, this thickened lining is shed, accompanied by bleeding. Bleeding usually lasts for 3-viii days. For most women, menstruum happens in a adequately regular, predictable blueprint. The length of fourth dimension from the first mean solar day of one menstruation to the beginning day of the side by side menstruum normally ranges from 21-35 days.
How does the menstrual cycle work?
The menstrual bicycle is controlled by a complex orchestra of hormones, produced by two structures in the brain, the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus forth with the ovaries.
If you just want a quick, general overview of the menstrual cycle, read this description.
For a more detailed review of the physical and hormonal changes that happen over the menstrual cycle, click here.
General overview of the menstrual bicycle:
The menstrual bike includes several phases. The exact timing of the phases of the cycle is a little bit dissimilar for every woman and can alter over time.
| Bike days (estimate) | Events of the menstrual cycle |
| Days one-five | The first day of menstrual haemorrhage is considered Day ane of the wheel. Your period can final anywhere from 3 to viii days, just 5 days is average. Haemorrhage is usually heaviest on the start 2 days. |
| Days 6-14 | Once the bleeding stops, the uterine lining (also called the endometrium) begins to prepare for the possibility of a pregnancy. The uterine lining becomes thicker and enriched in claret and nutrients. |
| Solar day 14-25 | Somewhere around 24-hour interval 14, an egg is released from ane of the ovaries and begins its journeying down the fallopian tubes to the uterus. If sperm are present in the fallopian tube at this time, fertilization tin can occur. In this example the fertilized egg will travel to the uterus and attempt to implant in the uterine wall. |
| Days 25-28 | If the egg was non fertilized or implantation does not occur, hormonal changes signal the uterus to prepare to shed its lining, and the egg breaks downwards and is shed along with lining. The cycle begins again on Mean solar day i menstrual haemorrhage. |
Comprehensive explanation of the menstrual bicycle:
The menstrual bicycle has three phases:
1. Follicular Phase (Days 1-xiv)
This phase of the menstrual cycle occurs from approximately day 1-14. Day 1 is the first mean solar day of bright red bleeding, and the end of this phase is marked past ovulation. While menstrual bleeding does happen in the early office of this stage, the ovaries are simultaneously preparing to ovulate again. The pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain) releases a hormone called FSH – follicle stimulating hormone. This hormone causes several 'follicles' to ascent on the surface of the ovary. These fluid filled "bumps" each contain an egg. Eventually, i of these follicle becomes dominant and within information technology develops a single mature egg; the other follicles shrink back. If more than than one follicle reaches maturity, this can lead to twins or more. The maturing follicle produces the hormone estrogen, which increases over the follicular phase and peaks in the mean solar day or two prior to ovulation. The lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes thicker and more enriched with blood in the 2d function of this stage (later on menstruation is over), in response to increasing levels of estrogen. High levels of estrogen stimulate the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which in turn stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH). On well-nigh mean solar day 12, surges in LH and FSH cause the egg to be released from the follicle. The surge in LH also causes a brief surge in testosterone, which increases sexual activity bulldoze, correct at the most fertile time of the wheel.
two. Ovulatory Stage (Day 14)
The release of the mature egg happens on about solar day fourteen as a consequence of a surge in LH and FSH over the previous twenty-four hours. Later on release, the egg enters the fallopian tube where fertilization may take place, if sperm are present. If the egg is not fertilized, information technology disintegrates subsequently about 24 hours. Once the egg is released, the follicle seals over and this is called the corpus luteum.
3. Luteal Phase (Days 14-28)
Afterward the release of the egg, levels of FSH and LH decrease. The corpus luteum produces progesterone. If fertilization has occurred, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone which prevents the endometrial lining from being shed. If fertilization has non occurred, the corpus luteum disintegrates, which causes progesterone levels to drop and signals the endometrial lining to begin shedding.
What is normal bleeding?
There is a range of normal bleeding – some women have short, light periods and others have longer, heavy periods. Your period may also change over time.
Normal menstrual bleeding has the following features:
- Your menses lasts for 3-eight days
- Your period comes again every 21-35 days (measured from the get-go 24-hour interval of one catamenia to the get-go day of the side by side)
- The total blood loss over the course of the period is around ii-3 tablespoons but secretions of other fluids can make information technology seem more
How can I figure out what is happening in my wheel? When am I ovulating?
Simply tracking your cycle on a calendar, along with some details of your bleeding and symptoms can aid y'all understand your bike. Record when your menses starts and ends, what the flow was like, and describe any pain or other symptoms (bloating, chest pain etc.), changes in mood or behaviour that yous experienced. Over several cycles you will exist able to see patterns in your cycle, or place irregularities that are occurring. Use your own calendar or try this 'menstrual diary'. There are also numerous apps available to help you track your flow. If your periods come up regularly every 21-35 days, chances are excellent that yous are ovulating.
 Beyond unproblematic calendar tracking, at that place are a few ways to figure out the timing of your own personal menstrual cycle. Separately or used together, these tin can exist used to aid determine when and whether you lot are ovulating. Iii methods you lot tin try are cervical mucus testing, basal body temperature monitoring, and ovulation prediction kits.
Beyond unproblematic calendar tracking, at that place are a few ways to figure out the timing of your own personal menstrual cycle. Separately or used together, these tin can exist used to aid determine when and whether you lot are ovulating. Iii methods you lot tin try are cervical mucus testing, basal body temperature monitoring, and ovulation prediction kits.
Cervical mucus testing
What is cervical mucus?
The cells lining your cervical canal secrete mucus. The consistency of this mucus changes over your bike. When you are fertile, the mucus changes to a consistency and structure that permits the sperm's travel on its way to your egg. When y'all are near fertile it will exist articulate, arable, and stretchy. To requite yous an thought of the consistency, this blazon of fertile fungus is sometimes abbreviated as EWCM – egg-white cervical mucus. When y'all are non fertile, the fungus is sticky, cloudy, and doesn't stretch.
How do I examination my cervical mucus?
Watching the changes in the corporeality and consistency of your cervical mucus can help y'all understand your cycle. Here's how information technology works: cheque your secretions before and after urinating by wiping with toilet paper. Alternatively you can insert a clean finger into your vagina to obtain a sample of fungus. Observe (and record) the consistency of the mucus, and use this chart to identify where you are in your cycle. Your mucus can exist cloudy, white, xanthous, or articulate. It can accept either a sticky or stretchy consistency. Use your thumb and forefinger to run across if the mucus stretches.
| Bike timing (approx) | Consistency of mucus | Fertility |
| Day v | No noticeable mucus | Not fertile |
| Day 5-eight | No noticeable mucus | Not fertile |
| Mean solar day eight-12 | Minimal, cloudy, sticky secretions | Not fertile |
| Solar day xiii-15 | Arable, articulate, wet, stretchy "egg-white" mucus | Fertile window – Earlier and during ovulation |
| Day 16-28 | No noticeable mucus | Not fertile |
You are most fertile on the days when yous have abundant, stretchy mucus. This is non a foolproof method to prevent pregnancy.
Basal Body Temperature
What does 'basal body temperature' mean?

Your basal trunk temperature is your lowest body temperature when you are at rest. Information technology is typically measured after several hours of sleep. As shortly every bit yous are upward and about, your temperature increases slightly.
How does the basal trunk temperature method of fertility tracking work?
This method takes a few months of daily tracking to plant the specific patterns happening in your trunk. Your body temperature changes slightly in response to hormonal changes related to ovulation. Before yous ovulate, your body temperature is usually between 36.two°C and 36.5°C. The day after y'all ovulate, your temperature volition increase by at least 0.v°C (36.7°C to 37.1°C for example) and stay at this temperature until catamenia. To utilize this method, mensurate and tape your torso temperature as soon as you wake up, subsequently at to the lowest degree 6 hours of sleep/rest. This means taking your temperature before you become out of bed and before eating or drinking annihilation. Take your temperature at most the same time every day. If y'all like to sleep in on the weekend you might have to ready an warning!
You will need a special "basal body temperature" thermometer, available at drug stores. Some thermometers take a memory characteristic that records the previous reading so yous don't accept to record it immediately. You will see the half-degree increase in temperature the 24-hour interval after you ovulate. This method will assist you determine if you are ovulating, how regular your bicycle is, and how long your cycle is.
If your temperature doesn't change over the class of your bike, and your periods are irregular, it is possible that y'all may non be ovulating. You lot may desire to get in touch with your health care provider.
Ovulation Prediction Kits
Ovulation prediction kits measure the concentration of the Luteinizing Hormone (LH) in your urine. This hormone is e'er present in small-scale amounts in your urine but increases in the 24-48 hours earlier ovulation occurs. More advanced kits as well measure estradiol, a course of estrogen that peaks on the day of ovulation. Instructions vary from kit to kit, so read the product insert carefully before using it.
Source: https://www.yourperiod.ca/normal-periods/menstrual-cycle-basics/